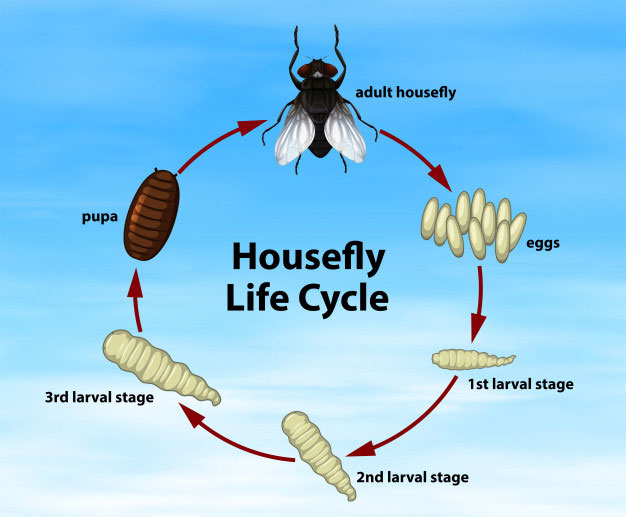
House flies
Housefly (Musca domestica) presence indicates insanitary conditions and this common pest spreads dysentery, diarrhoea, cholera, typhoid, and salmonellosis.
Flies use their sponging mouth parts to suck liquids thar their saliva generates from solid food. When flies land on a surface they defecate and regurgitate on it. Flies can land on food after visiting unhygienic places and spread disease pathogens through food. Flies have spurs or hairs that are convenient perch to disease causing bacteria.
Humans despise flies for the latter being carriers of illness inducing germs and for being indicative of insanitary conditions. In nature, flies are important as pollinators but in human habitats, flies are harbingers of ill-health.
Managing house flies through an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach requires forethought and action.
Conventional IPM steps for any pest apply to treating flies too and are: prevention, monitoring and control by pesticide application and we describe the first two steps in detail below.